ADOT utilizes GIS to manage information, analyze and plan
ADOT utilizes GIS to manage information, analyze and plan
ADOT utilizes GIS to manage information, analyze and plan
ADOT utilizes GIS to manage information, analyze and plan
If you need more information about ADOT's GIS Analytics, please visit:
/planning/transportation-analysis/gis-analysis
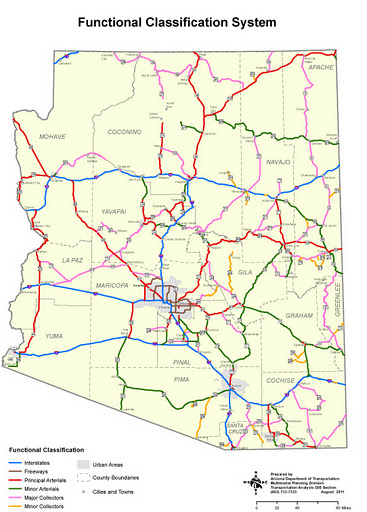
An example of a map available
on ADOT's site.
The saying, “a photo speaks 1,000 words” holds true when it comes to data.
Because, for most people (we’re not talking about the engineers who are out there reading this!) it’s hard to pull real meaning from just a long list of numbers.
But, when you feed those numbers and information into map (it’s sort of like a photo, right?), you start to find relationships between the data.
At least, that’s the super-simplified idea behind Geographic Information Systems, a.k.a. GIS, which ADOT uses to plan, analyze, model and manage information.
ADOT’s GIS Section Manager James Meyer explains GIS as being similar to a database, but because it has a spatial element – meaning you can plot several layers worth of data onto a map – GIS is very valuable in reaching conclusions and making decisions.
For instance, ADOT could plot traffic count data onto a map along with another layer that gives pavement condition scores. From there, it would be easy to “see” where and how traffic affects the road conditions, leading to planning and funding choices.
Some of the ways ADOT utilizes GIS …
ADOT’s GIS section updates, verifies and maintains the Arizona Transportation Information System (ATIS), which is the basis for all GIS work at ADOT.
It contains a linear referencing system that can take all of ADOT’s route and milepost data and display it on a map. Meyer calls ATIS the backbone of roadway inventory data that gives a common point of reference allowing you to tie all data to a common factor – the road’s centerline.
The Highway Performance Monitoring System (HPMS) is another way ADOT uses GIS.
HPMS is a report submitted annually to the Federal Highway Administration. It contains data on every single road in the state. Some of this data includes traffic counts, ownership, surface type, etc. HPMS is used as a planning tool by FHWA and as an aid for determining the amount of federal funds that will be distributed to each state.
ADOT’s GIS section employees also provide mapping support to all of ADOT. The maps they produce go into studies, presentations and “what-if” scenarios for pre-construction that can show planners where the future roads will be and what they’ll be next to.